Environmental Initiatives
Specific Initiatives
The Tokyo International Forum strives in various ways to leverage natural energy, use energy efficiently, and create a comfortable environment.
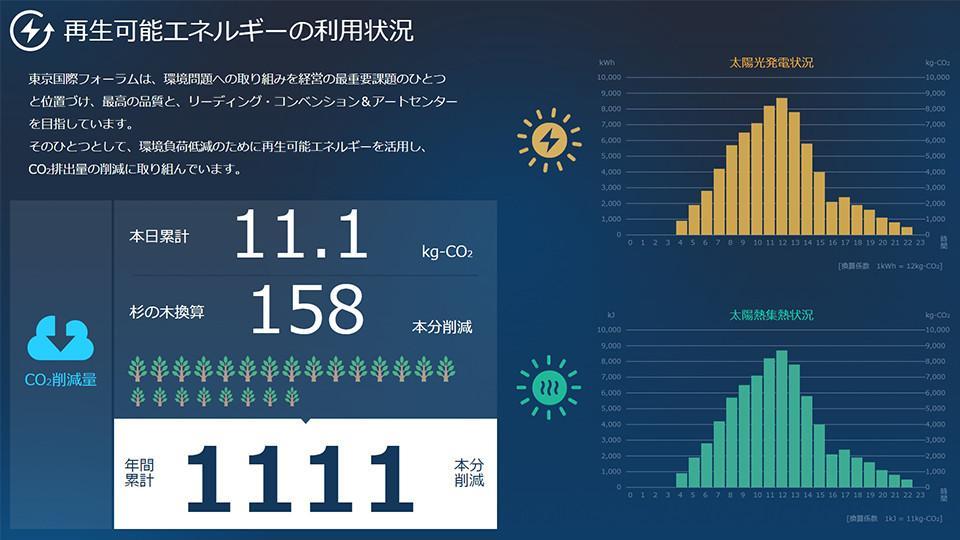
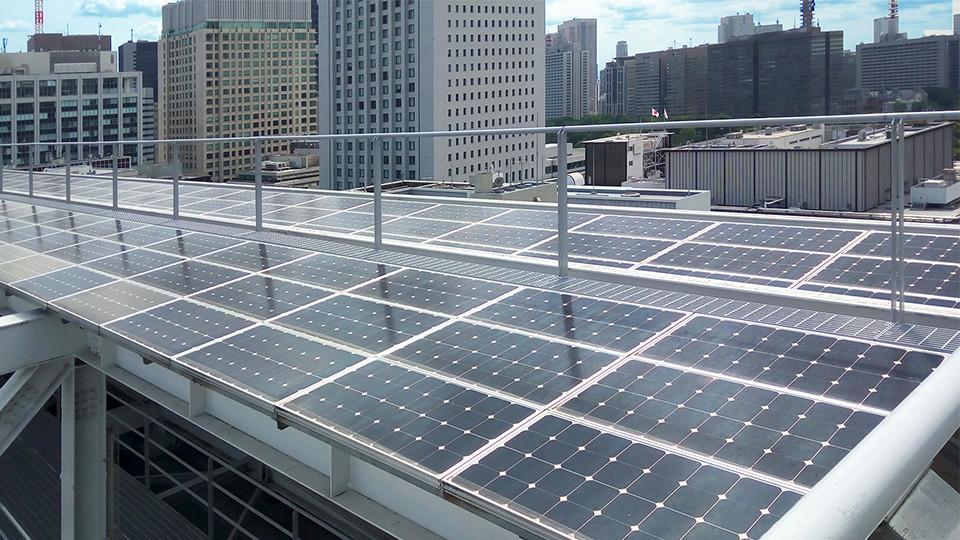
Solar Power Generation System
Solar panels are installed on the roofs of the Hall Buildings. The power they generate is converted to AC power and used in the buildings.
The solar panels, about 600 square meters in area, have generation capacity of 93kW.
This is equivalent to the electricity used in nearly 50 standard households.

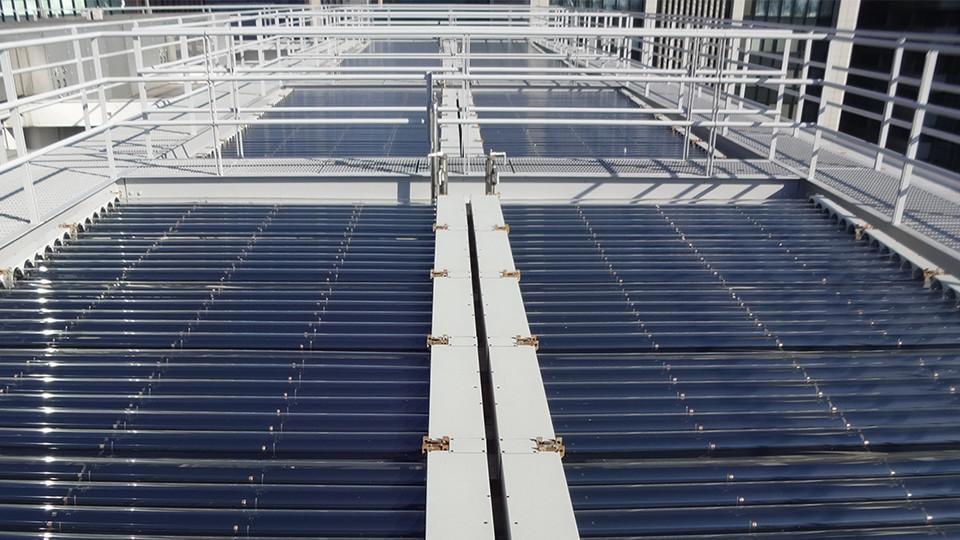
Solar Heat Collecting System
Apart from the solar power generation system, the hall roofs are also equipped with evacuated glass tube solar thermal collectors. Water that has been heated using solar heat is supplied to restrooms and showers in the buildings, as well as to restaurant kitchens.
The heat collecting system is about 400 square meters and temperature is 85℃.
The heat collected is sufficient to heat water in about 500 bathtubs to a temperature of 40℃.

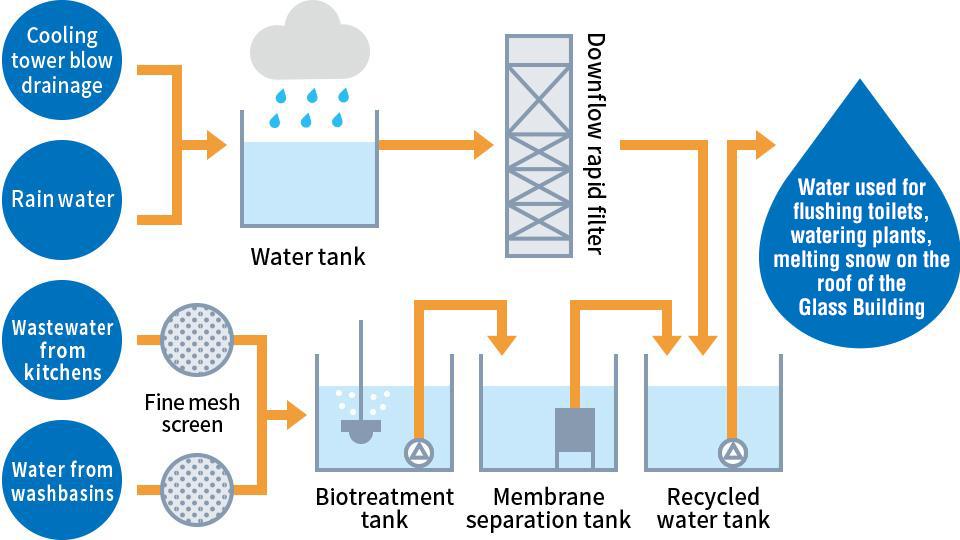
Waste Water Recycling System
Waste water generated in the buildings (water from washbasins or restaurant kitchens) and rain water collected on the premises are processed (biotreatment and membrane separation) in a waste water recycling system and used to flush toilets, water plants, and melt snow that has accumulated on the roof of the Glass Building.
Utilization rate of recycled water: About 90% of the water is used for flushing toilets and other purposes (subject to seasonal variations).
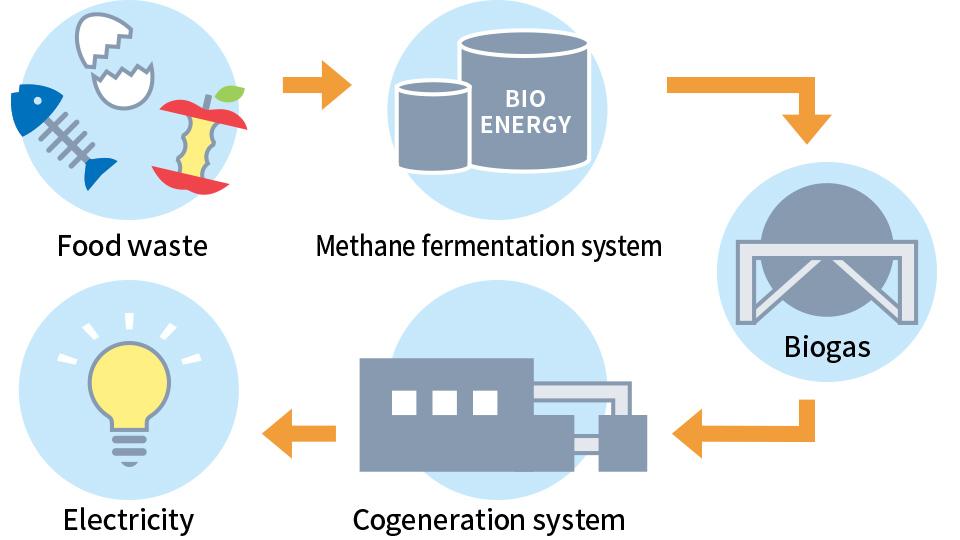
Food Waste Recycling
Food waste generated by the restaurants and catering in the facilities is recycled and transformed into electrical energy, etc. Collected food waste is transported to a recycling plant in Ota City where it is transformed into biogas via methane fermentation technology. Biogas is then used in the factory’s cogeneration system to produce energy in the form of electricity.
Most of this electricity is then sold to the community surrounding the recycling plant.
We also strive to thoroughly separate and reduce other garbage produced in the facilities.
Energy-Saving in Lighting and Air Conditioning
Lighting equipment in seating areas, lobbies, corridors, and other spaces are being changed to LED lights, which consume less power and last longer. We strive to save more energy by using highly energy-efficient permanent magnet motors for air blowers and introducing a system that optimizes the intake of outdoor air for air conditioning.
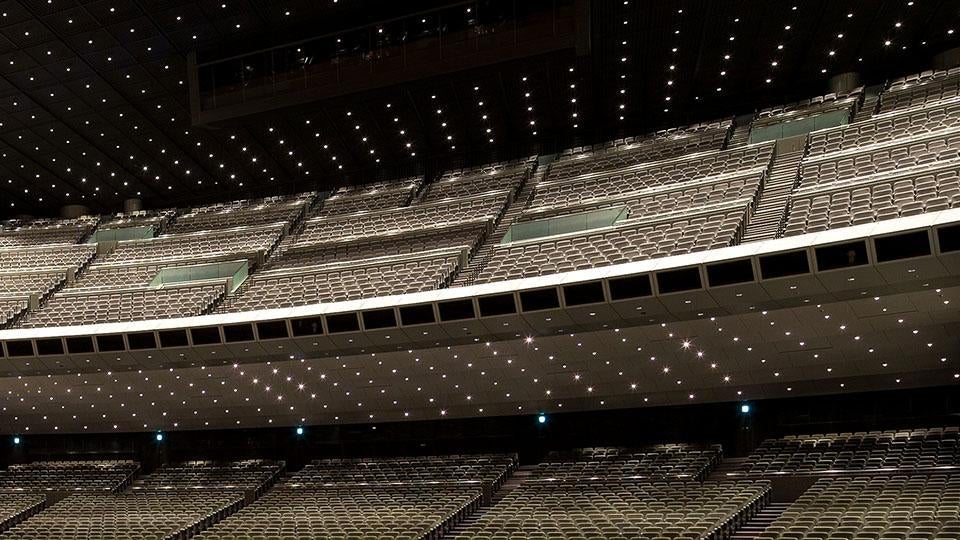

Ceiling lights (LED) in Hall A
Energy Management System (EMS)
To achieve energy-efficient operations while maintaining a comfortable, convenient environment for visitors, an energy management system (EMS) is used to optimize operation of all equipment in the building including air conditioning.
Tokyo International Forum tracks its usage of renewable energy on a real-time basis and displays it with digital signage devices onsite to clearly disseminate information about its environmental activities.